Published on: July 5, 2021
5G networks are being widely deployed and we can take a realistic view of how this new technology can shape the world over the next 10 years. The advent of 5G is not only a generational step in wireless networks but it opens the door to the future of a fully connected world and possibilities of evolution in the industry. Recent advances in computing power have led the connected ecosystem towards more powerful technologies, services, and providers than ever before with low latency and high reliability.
Remote Surgery
In January of 2019, China completed the world’s first 5G remote surgery. A key enabling factor for this important achievement was the low delay, in the milliseconds’ range facilitated by the 5G network. The high data rates and reliability provided by 5G network can significantly accelerate the development of the telehealth field. This technology has the potential to transform the wider surgical industry with huge benefits for patients. In addition to this, by exploiting the 5G capability to support massive Internet of Things (IoT) devices and smart city infrastructures, it will be possible to provide services like remote patient monitoring and health care assistance. The ongoing pandemic which has overburdened hospitals and medical staff indicates the benefits of a real-time connected infrastructure, where patients can be treated remotely at home and give us a glimpse into the future of the healthcare system.
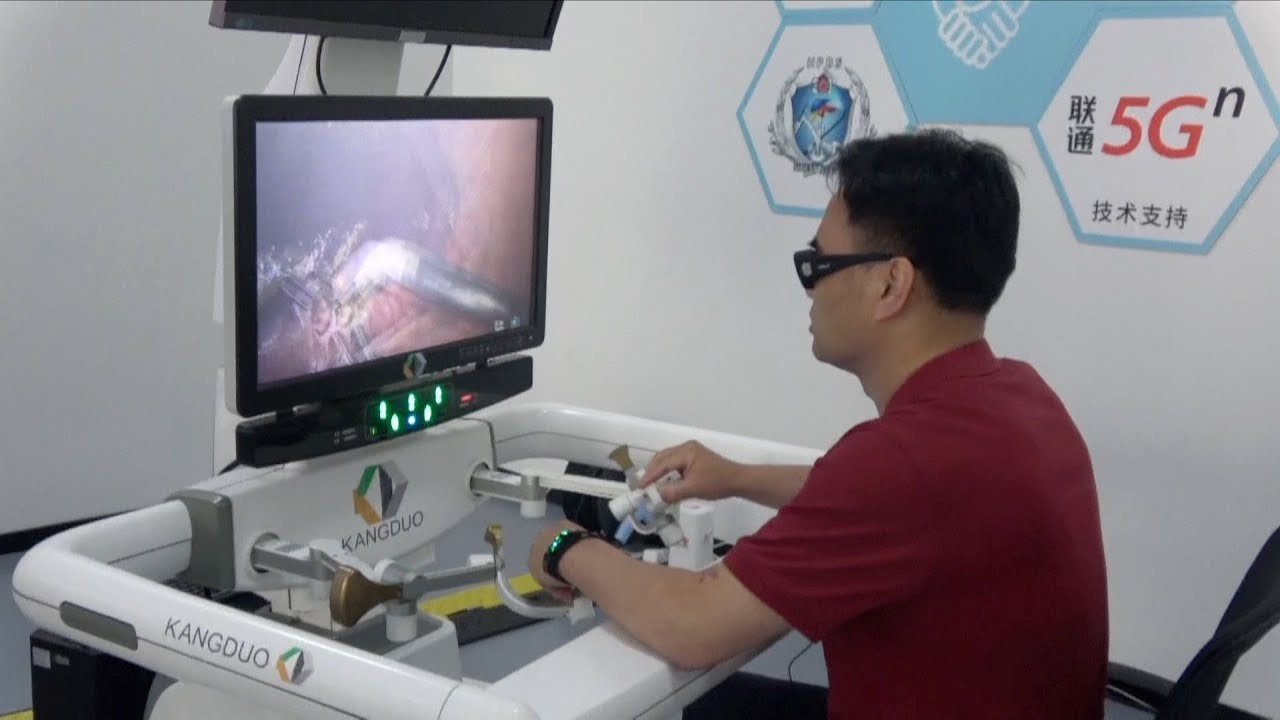

Figure 1: World’s first 5G remote surgery in China [1]
Industry 4.0
Intelligent industry processes and networking of machines led by the improvements in 5G are referred to as Industry 4.0. This means automation of industries and requires real-time communication between machines that will generate petabytes (1015 bytes) of data. To achieve this, the 5G infrastructure is going to benefit from technology advancements in big data handling, connectivity and automation. With features such as low latency, ultra-high reliability and high bandwidth, Industry 4.0 will lead to smart warehouses and distribution center’s that can handle growing consumer demands much faster.
Figure 2: New Industry 4.0 and 5G [2]
Industry 4.0 foresees the growing trend towards automation and data exchange in technology and processes within the manufacturing industry, including:
- The Internet of Things (IoT)
- The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
- Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
- Smart manufacture
- Smart factories
- Cloud computing
- Cognitive computing
- Artificial intelligence
This automation creates a manufacturing system whereby machines in factories are augmented with wireless connectivity and sensors to monitor and visualize an entire production process to make autonomous decisions. Wireless connectivity and the augmentation of machines will be greatly advanced by the full rollout of 5G. This will provide faster response time, allowing for near real-time communication between systems.
Virtual Reality
A study made by Intel predicts that 5G will drive $1.3 trillion in new revenue from the media and entertainment industry by 2028 [3]. VR/AR is the future of the entertainment industry but VR applications are sensitive to network performance and require a more reliable network with lower latency. 5G networks can provide such strict latency and reliability requirements and that is why 5G is considered to be a major player in unfolding the future of the entertainment industry.
 Figure 3: Intel 5G: The economics of entertainment [3]
Figure 3: Intel 5G: The economics of entertainment [3]
VR/AR will introduce a new way for people to interact with media through virtual items, virtual characters and augmented contextual information while allowing content creators to reach new audiences [4].
5G-led innovations will enable mobile cloud gaming (cloud-based interactive games that use mobile devices to process game scenarios), as it is fast, offers high-resolution graphics and allows for real-time streaming. You’ll be able to experience fully interactive gaming with 5G in both the technical and economic sense. Moreover, 5G will bring new senses to the media, e.g. wearing responsive haptic clothing merged with advanced AR/VR capabilities will allow a person to fully immerse themselves in the play. 5G will also help to improve driving experience. A combination of network capacity, low latency, and localized storage will improve the car connectivity at high speed and reduce stalling and network lag. Creating 5G hotspots could create new business models, including drivers being able to download maps or movies or upload car diagnostic data, while at highway rest stops or gas stations.
Contributing towards the technology advancements in every field, 5G will provide intelligent optimization based on services and user awareness and will improve energy and cost efficiency by over a hundred times.
If you were able to stick until the end and can’t wait for more content and you also want to know about us and our projects, you can always follow our social media channels.
References
[2] https://www.eit.uni-kl.de/wicon-tmp/new-industry-4-0-projects/
[4]https://newsroom.intel.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2018/10/intel-5g-economics-backgrounder.pdf





